 Process
Analysis Toolkit (PAT) 3.5
Help Process
Analysis Toolkit (PAT) 3.5
Help |
Critical system requirements like safety, liveness and fairness play
important roles in software/system specification, development and testing. It is
desirable to have handy tools to simulate the system behaviors and verify
critical properties. Process Analysis
Toolkit (also known as PAT) is design to apply state-of-the-art model
checking techniques for system analysis. It supports reachability analysis,
deadlock-freeness analysis, full LTL (linear temporal logic) model checking,
refinement checking as well as a powerful simulator. It is a user-friendly model
checker for Windows users. Starting from PAT 2.0, we applied a layered design to support the analysis of
the different system/languages. The figure below shows the architecture design
of PAT. For each supported system (e.g., distributed system, service oriented
computing, bio-system, security protocols, sensor network and real-time system),
a dedicated module is created in PAT, which identifies the (specialized)
language syntax, well-formness rules as well as (operational) formal semantics.
The formally defined operational semantics of the target language translates the
behaviors of a model into a Labeled Transition System (LTS). During this
translation, domain specific abstraction can be applied to the input model,
e.g., data abstraction, zone abstraction and environment abstraction. LTS serves
as the internal representations of the input models, which can be automatically
explored by the verification algorithms or used for simulation. If there is any
counterexample is identified, then it can be animated in the simulator. The
advantage of this design allows the developed model checking algorithms to be
shared by all modules. This architecture allows new languages to be developed easily by providing
the syntax rules and semantics. Till now, eleven modules have been
developed, namely Communicating Sequential
Processes (CSP) Module, Real-Time System
Module, Probability CSP
Module, Probability RTS
Module, Labeled Transition System
Module, Timed
Automata Module, NesC Module, ORC Module, Stateflow(MDL)
Module, Security Module
and Web Service
(WS) Module. In the future, our targeted systems include distributed
systems, UML (state chart and sequence diagrams) and so on. The main functionalities of PAT are listed as follows: PAT has been applied to a variety of different systems to prove properties or
identifying bugs. Indeed, previously unknown bugs have been found using PAT. We
have successfully demonstrated PAT as an analyzer for process algebras in the
30th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2008) [LiuSD08] and the
21st International Conference on Computer Aided Verification (CAV 2009) [SunLDP09]. In
summary, PAT is a self-contained framework for automated analysis on concurrent
and real-time systems.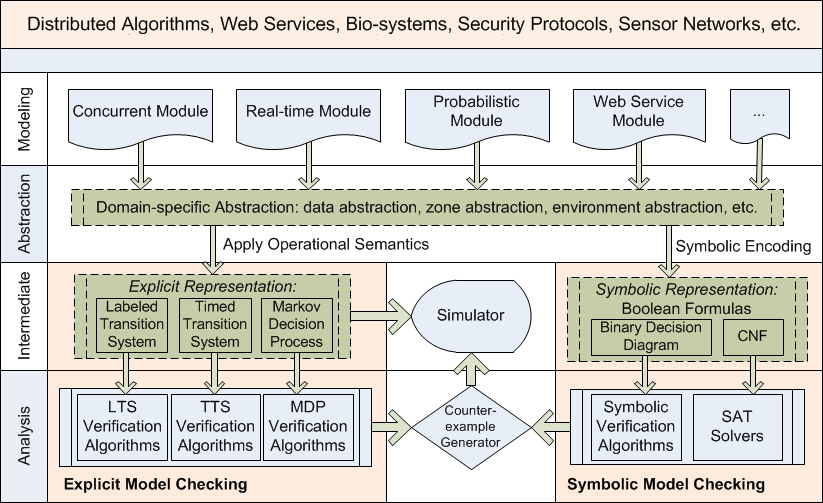
Copyright © 2007-2012 Semantic Engineering Pte. Ltd.